Environmental Impact of Nuclear Energy
4 minute readNuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.
Home > Learning Center > Energy Production > What Are Small Modular Reactors?
5 minute read • Last update May 2024
It’s no secret that global concerns over climate change have escalated in recent years. But what you might not know is that ongoing discussions regarding sustainable energy solutions have led to a reevaluation of nuclear power, with small modular reactors emerging as a viable option.
But, precisely what is a small modular reactor (SMR), and how can nuclear energy help our society meet increasing electricity demand while minimizing environmental impact and enhancing safety standards?
We’ll level with you. SMR technology can be a complex topic. However, in this handy guide, we’ll break everything down in simple terms to help you gain a more comprehensive understanding. We’ll cover:
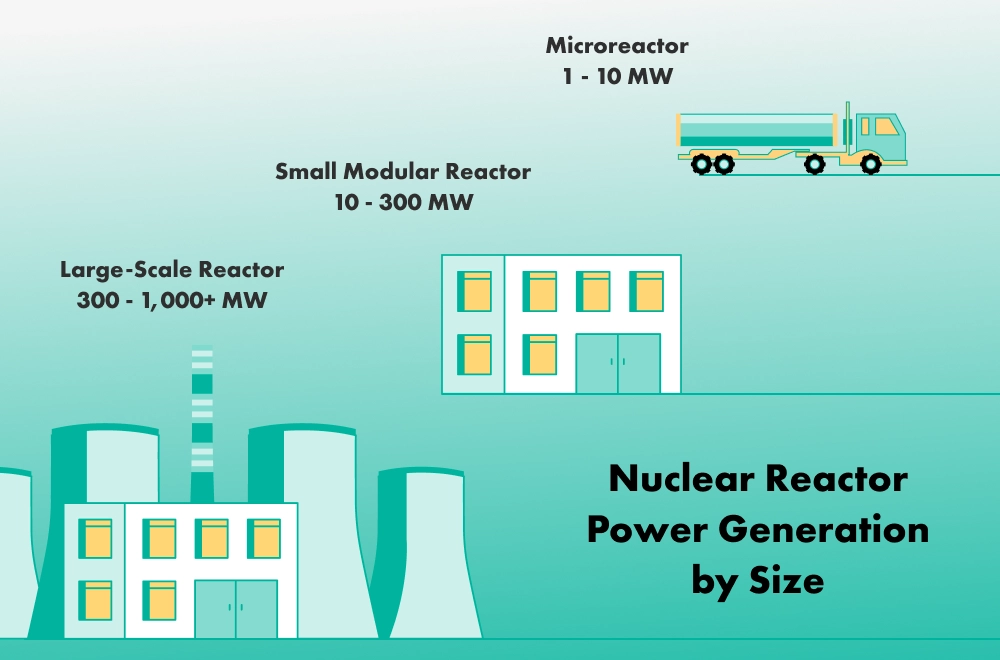
Small modular reactors are an advanced nuclear reactor with a smaller physical size and energy output capability than a typical, larger reactor at a nuclear energy plant.
The terms small modular reactor (SMR), small nuclear reactor, and modular nuclear reactor are often used interchangeably to describe compact, flexible nuclear power plants.
What distinguishes small modular reactors from conventional plants is their size, design, and deployment approach. These differences are typically better understood by defining each element in more detail:
Before moving on from terminology, it’s essential to note that while SMRs have a few interchangeable descriptors, small modular nuclear reactors and micro nuclear reactors are not the same.
As the name suggests, a micro nuclear reactor is an even smaller type of power plant. Essentially a mini version of a small modular nuclear reactor, the typical output of micro modular reactors is just 10 MWe of electricity.
Micro power plants are compact enough to be portable and are designed for electricity generation in niche applications or in remote regions where traditional power generation is impractical or unavailable, like at military bases or industrial sites.
Yes, a few small modular reactors are already operational. China and Russia were the first locations to get these up and running. Russia’s floating nuclear power plant, operated by OKBM Afrikantov, began power output in May 2020. Meanwhile, the China Huaneng Group connected their SMR nuclear plant to the grid in December 2021.
While there are only a handful of fully operational SMRs at present, around 90 more scheduled for future deployment are currently in the design phase, under construction, or awaiting licensing. Planned small modular nuclear reactor sites span the globe, although the lion’s share will be located across North America, Europe, and Asia.
It’s worth noting that the development process for SMR technologies is complex, involving significant nuclear energy research. There is still much work to be done and hurdles to overcome to ensure a viable and sustainable energy transition as we move away from fossil fuel reliance. With that in mind, let’s explore a comprehensive list of small modular reactors’ pros and cons.
Small modular reactors offer several advantages over traditional nuclear power. Let’s review the various benefits in detail.
SMRs have a smaller physical footprint compared to conventional nuclear reactors, allowing for more flexible siting options in urban environments and areas with limited space. Co-location with existing infrastructure and the potential for integration in industrial processes further enhance their flexibility.
By leveraging modular construction techniques and standardized designs, small nuclear reactor designers can achieve economies of scale. Factory-based manufacturing streamlines construction and deployment processes, accelerating project timelines and reducing overall costs.
Modular designs allow for incremental capacity expansion, enabling operators to scale up or down based on electricity demand. Additionally, SMRs can provide reliable energy in a variety of settings, including grid-connected systems, remote communities, municipal power systems, industrial facilities, and military installations like naval reactors.
Smaller reactors incorporate advanced nuclear safety features to mitigate the risk of catastrophic accidents associated with large power reactors. For example, many utilize passive safety systems that rely on natural phenomena like gravity or convection to cool the reactor core without human intervention in the event of a shutdown.
Small modular systems have lower resource requirements, which minimize land disturbance and material usage. Additionally, SMRs can integrate renewable, low-carbon power sources into hybrid systems, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
While SMRs represent a significant milestone in the development of nuclear energy, several challenges remain. Here’s a list of the primary concerns.
SMR licensing requires more regulatory approvals and oversight than conventional plants. However, as SMRs are a relatively new technology, regulatory agencies and federal government bodies may lack standardized guidelines and frameworks necessary for accurately assessing safety and performance. This can lead to increased uncertainty and complexity in the licensing process.
While small modular nuclear reactors incorporate advanced safety systems, they are not immune to the risks associated with nuclear power generation. In other words, despite their passive safety features, accidents and malfunctions can still occur, posing potential risks to public health and the environment.
The lower power output of small modular reactors equates to smaller economies of scale, meaning the cost per unit of electricity generated may be higher than that of larger reactors, particularly in the absence of widespread deployment and standardized designs.
Like any other nuclear industry process, SMRs generate radioactive waste during operation. Therefore, specialized nuclear waste management strategies are essential to ensure the proper handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive materials, as well as the safe dismantling and decontamination of site facilities.
Just like their larger industrial counterparts, small reactors raise concerns about nuclear proliferation, energy security, and the potential misuse of materials and technologies for weapons development. Therefore, implementing industry safeguards, export controls, and non-proliferation measures are critical in promoting international cooperation and transparency.
The compact size, modular design, and versatility of small nuclear reactors make them well-suited for integration with intermittent renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power. These reactors contribute to enhanced grid stability and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, small nuclear reactors offer multiple opportunities for innovative applications beyond electricity generation, including:
Currently, there is significant government support for improving SMR technology, developing more advanced nuclear reactors, and addressing the remaining challenges that stand in the way of commercialization. Collaborative initiatives between industry, academia, and federal agencies are widely considered to be the key to sustainable development and the transition to a low-carbon energy future. In the US, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission is at the forefront of developing regulatory policies regarding design, licensing, and inspection.
If you’re interested in learning about how small modular reactors are shaping the future of the electrical power grid, you might also be interested in exploring cleaner and more affordable energy solutions for your home.
BKVE is committed to innovation, offering solutions that leverage the latest technologies to ensure cost-effective electricity for our customers. Check out our range of fairly priced and straightforward energy plans today!
Graham Lumley, Digital Marketing Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 8 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

Nuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.

Discover the different types of nuclear power plants and how they work
Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.