Environmental Impact of Hydropower
3 minute readHydropower offers clean electricity but also alters ecosystems, water quality, and greenhouse gas levels.
Home > Learning Center > Energy Production > What Is Wave Power?
4 minute read • Last update March 2025

Wave energy (or wave power) harnesses the ocean’s waves to generate energy by converting a wave’s kinetic energy into electricity. Wave power is a form of renewable and sustainable energy that’s often overlooked but has immense potential.
Wave power has potential cost benefits over solar and wind, but faces technological obstacles limiting its large-scale adoption for applications such as generating electricity and water desalination.
Wave power begins with wind, which is caused by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface.
Warm air rises and expands, creating areas of low pressure compared to places with cooler air. Air then begins to move from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas. This movement of air is wind!
As wind rushes across the surface of the Earth, it creates waves in oceans around the globe. We can harness the movement of the waves to generate electricity.
Wave power is based on interactions between ocean waves and energy converters, specifically engineered to harness wave energy.
Waves are moving, so they contain kinetic energy. That kinetic energy can be used to drive movement in special devices that are placed on or just below the surface of the ocean, such as:
Wave energy devices are the tools that allow us to effectively harness wave energy by transforming the kinetic energy of waves into usable electricity.
These devices, like point absorber buoys, oscillating water columns (OWCs), and overtopping devices, each have unique mechanisms for capturing and converting wave energy.
Let’s examine these devices in more depth, uncovering the process through which they convert ocean waves into a renewable energy source.
Imagine a buoy bobbing in the ocean, rising and falling with the waves. This is more than just a floating device; it’s a point absorber buoy, a device designed to generate electricity by harnessing the energy of ocean waves.
These buoys use a floating cylinder to capture the vertical movement of waves, which is then harnessed through a cable anchored to the seabed. This up and down motion is subsequently transformed into electricity via converters such as alternators, linear generators, or hydraulic systems.

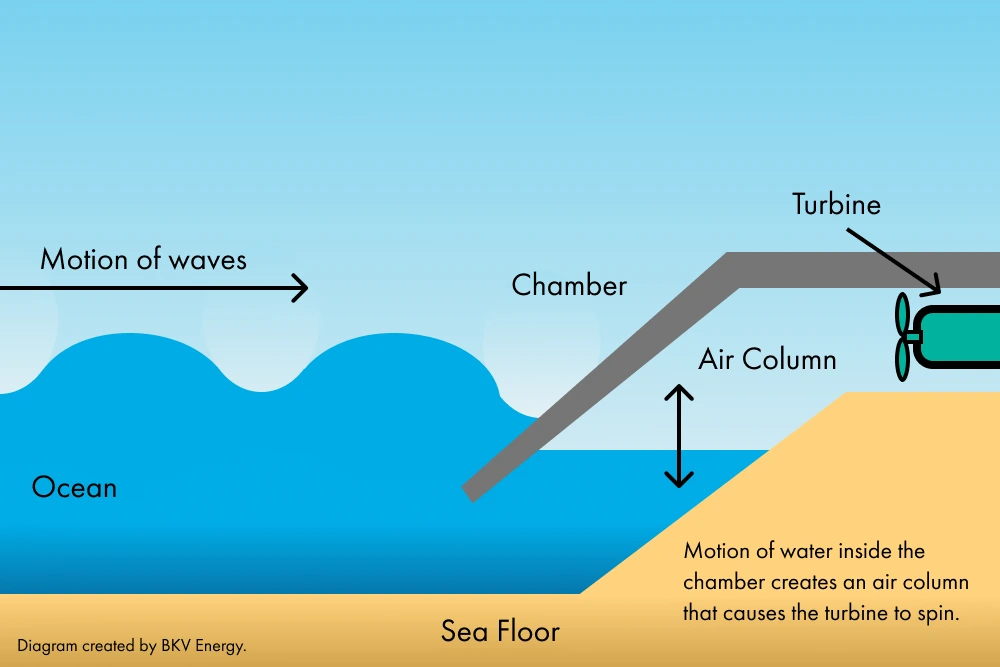
Another intriguing wave energy device is the Oscillating Water Column (OWC), a device that uses wave power to generate electricity. These devices use the rise and fall of waves to compress air, which then drives a turbine to produce electricity.
As the waves rise and fall, the air in the column is forced to move, creating a strong air flow that can power turbines.
The last of the wave energy devices we’ll explore are overtopping devices.
These devices harness wave energy by allowing waves to flow into a reservoir, which then releases the water through turbines to generate electricity.
Factors that can influence the efficiency of overtopping devices include:
Despite potential drawbacks, such as lower energetic wave content, overtopping devices offer a promising approach to harnessing wave energy.
Although they both belong to the category of ocean energy, tidal and wave energy are distinct forms of energy that utilize different methods and technology to capture the motion of the ocean.
Tidal turbines and tidal barrages serve to capture tidal energy, whereas wave energy employs devices such as oscillating water columns, point absorbers, and terminators to transform wave energy into electrical power.
Despite their differences, both sources of energy continue to play a crucial role in our quest for renewable energy sources.
Despite the significant benefits of wave energy, we must also take into account its potential environmental impact. Although it is generally considered a clean energy source with no greenhouse gas emissions, wave energy conversion can affect marine habitats,
However, concerns remain about potential impacts of wave energy converters, including:
Wave energy presents an attractive opportunity in the renewable energy sector, theoretically possessing the capability to fulfill a substantial part of global power requirements.
With wave energy development on the rise, it offers reliable and steady power generation, enhancing predictability in energy supply.
Nonetheless, the journey towards harnessing wave power is not devoid of obstacles:
Despite these challenges, the potential of wave energy remains largely untapped and holds immense promise for our renewable energy future.
In comparison with other renewable energy sources, wave energy exhibits its own distinct set of pros and cons.
While it offers a more dependable and consistent output compared to wind energy, it also comes with higher initial costs and the requirement for effective energy converters.
Despite these challenges, wave energy holds potential cost benefits over solar and wind energy.
However, its adoption is currently less widespread, and it faces technological obstacles in expanding on a significant scale.
Wave power extends beyond theoretical concepts, manifesting itself in practical, real-world applications. Some examples of wave power projects include:
Graham Lumley, Digital Marketing Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 8 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

Hydropower offers clean electricity but also alters ecosystems, water quality, and greenhouse gas levels.

Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.