Environmental Impact of Nuclear Energy
4 minute readNuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.
Home > Learning Center > Energy Production > Nuclear Fusion vs Fission: Difference Between Reactions
2 minute read • Last update April 2024
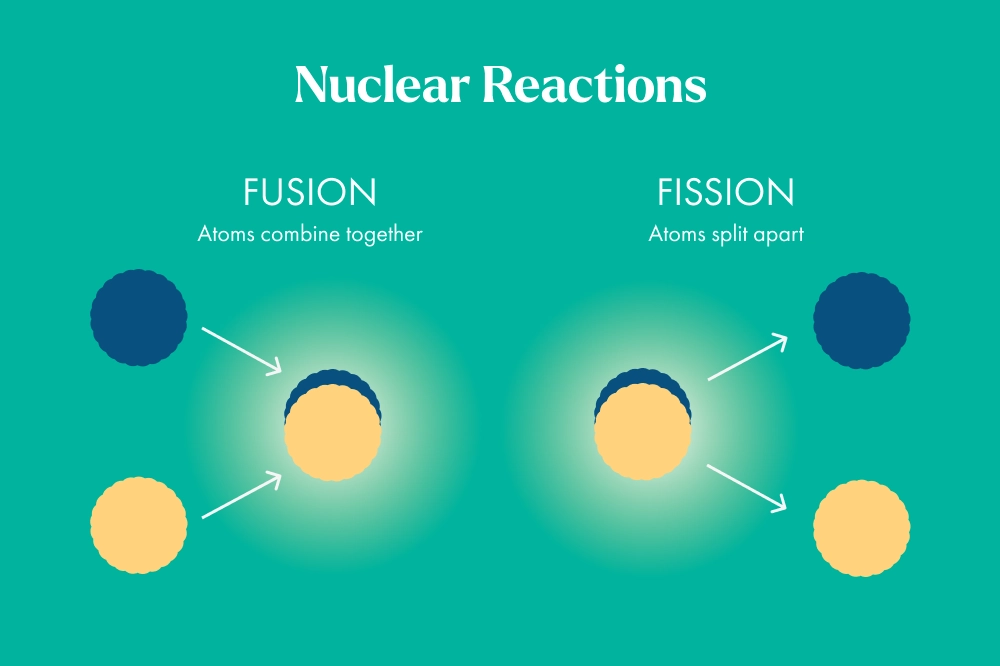
Nuclear fusion occurs when two atoms fuse together, or combine, into a larger atom. This fusion process releases a great amount of energy. Nuclear fission occurs when one atom is ripped apart into smaller atoms. Fission and fusion both release a great deal of energy, but fusion releases about four times more.
| FUSION | FISSION | |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction | Atoms fusing together | Atoms splitting apart |
| Energy Released | 4X more than fission | 4X less than fusion |
| Radioactive Waste | Does not produce | Produces |
| Electricity Generation | Not used commercially | Used commercially |
If you look up into the sky during the day, you can see a huge nuclear reactor that’s powered by nuclear fusion: the sun.
Because the sun is enormous (over 1.3 million Earths can fit inside), it has a lot of gravity. That high level of gravity creates enough pressure to force atoms to slam into each other, forming larger atoms. One example of this is two hydrogen atoms fusing together to form helium.
On Earth, scientists are attempting to recreate nuclear fusion to generate electricity. This would be an advancement in power production technology because all existing nuclear plants are powered by fission. In the last couple years, scientists have made large steps forward in achieving this goal. In December 2022, U.S. Department of Energy scientists were able to produce more energy than they put into a nuclear fusion reactor for just a few seconds. They were successful again in August 2023.
In nuclear power plants around the globe, nuclear fission is induced by throwing neutrons at uranium atoms at high speeds. The impact is so strong it causes the uranium atoms to split, which releases a lot of energy. When the uranium atom splits, more neutrons are released and they continue to collide with other uranium atoms. It’s a chain reaction that repeats itself over and over again.
Graham Lumley, Digital Marketing Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 8 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

Nuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.

Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.