2026 Atlantic Hurricane Season Name List
2 minute readThe 2026 hurricane season, starting June 1, 2026, and ending November 30, 2026, is rapidly approaching. Here’s the list of
Home > BKV Energy Blog > All Posts > Hurricanes vs Typhoons: What’s the Difference?
3 minute read • Last update July 2025
Hurricanes and typhoons are the same type of storm, a tropical cyclone, but they are given different names based on where they occur.
Hurricane is the term used for storms that mostly impact the Caribbean, the United States, Mexico, and Central America. These storms form and travel through the North Atlantic, the Central North Pacific, and the Eastern North Pacific.
Typhoon is the term used for storms that mostly impact Japan, the Philippines, China, Taiwan, and Korea. Cyclones in this part of the world form over the Northwest Pacific Ocean.
As the primary difference between a hurricane and typhoon is geographical, they are very similar. Both are characterized cyclical motion around a low-pressure center, high winds, heavy rain, and storm surges.
| Hurricanes | Typhoons | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of storm | Tropical cyclone | Tropical cyclone |
| Oceans | North Atlantic, Central North Pacific, Eastern North Pacific | Northwest Pacific |
| Regions impacted | United States, Mexico, Central America, Caribbean | Japan, China, Taiwan, Korea, the Philippines |
Tropical cyclones form in other areas around the globe as well, such as the South Pacific and Southeast Indian Ocean, North Indian Ocean, Southwest Indian Ocean, near Australia, and Southern Pacific Ocean.
In these regions, the cyclical storms are simply referred to as cyclones or tropical cyclones.
While both monsoons and tropical cyclones (also known as hurricanes and typhoons depending on the location) are significant atmospheric phenomena resulting in wind and heavy rain, they differ rather drastically in their nature, formation, and impact.
A tropical cyclone is a rotating, organized system of clouds and thunderstorms that originate from in tropical or subtropical seas. They form as a result of a combination of warm sea surface temperatures, low air pressure near the Earth’s surface, reduced vertical wind shear, and the Coriolis effect. These storms, often 180-300 miles wide, have intense rain and wind rotating around a central eye that lead to flooding, storm surges, and wind damage. Cyclones are typically short-lived storms, lasting a few days to a couple weeks.
On the other hand, a monsoon is a seasonal wind pattern that can last months, dropping heavy rain as a result of mismatched heating of land and sea. During the summer, land heats up more quickly than the ocean, causing air over the land to warm and rise. This creates a low pressure area that draws in most air from the ocean, which leads to have rainfall.
Unlike a cyclone, monsoons have lower speeds, do not revolve around a central eye, and can last several months while impact entire countries or continents. A tropical cyclone will impact a comparatively much smaller area.
| Hurricanes | Monsoons | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of weather pattern | Tropical cyclone | Seasonal wind and rain |
| Energy source | Warm sea surface temperatures, low air pressure, reduced vertical wind shear, Coriolis effect | Difference in temperature between land and sea during the summer |
| Size and duration | Several hundred miles wide, lasting days to weeks | May impact an entire country or continent, can last months |
Tornadoes and hurricanes are both types of rotating weather phenomena, but they have several major distinctions between them.
First, hurricanes and tornados have significant different sizes. A hurricane may be up to 300 miles wide, but tornadoes are much smaller, typically several hundred feet wide. The largest tornadoes may have a diameter just over a mile.
Next, tornadoes are much more short-lived than hurricanes. While a hurricane may last a couple weeks, a tornado may last a few minutes to an hour.
These weather patterns also derive their energy from very different sources. As mentioned previously, a hurricane uses warm ocean water as fuel. A tornado forms as a result of atmospheric instability from a land-based thunderstorm.
Finally, there is a major difference in potential wind speed. Tornadoes have the highest wind speeds on Earth. The tornado with greatest wind speed every record was over 300 miles per hour in Oklahoma in 1999. The highest wind speed recorded from a hurricane was 190 miles per hour, set in 1980 by Hurricane Allen. A category 5 hurricane will never approach the high wind speeds of the fastest tornados.
| Hurricanes | Tornadoes | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of weather pattern | Tropical cyclone | Wind rotation in a thunderstorm |
| Energy source | Warm sea surface temperatures, low air pressure, reduced vertical wind shear, Coriolis effect | Atmospheric pressure differences in a thunderstorm |
| Size and duration | Several hundred miles wide, lasting days to weeks | Several hundred feet to a mile wide, lasting minutes to an hour |
| Wind speed | Up to 190mph | Up to 300mph |
If you live in Texas are looking to save money on your monthly electricity bills, consider switching to BKV Energy. Our Bluebonnet plan is simple, affordable, has fewer fees and more benefits. Texans can save up to $800 per year by switching. Enter your zip code to explore rates near you.
Graham Lumley, Growth Product Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 10 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

The 2026 hurricane season, starting June 1, 2026, and ending November 30, 2026, is rapidly approaching. Here’s the list of
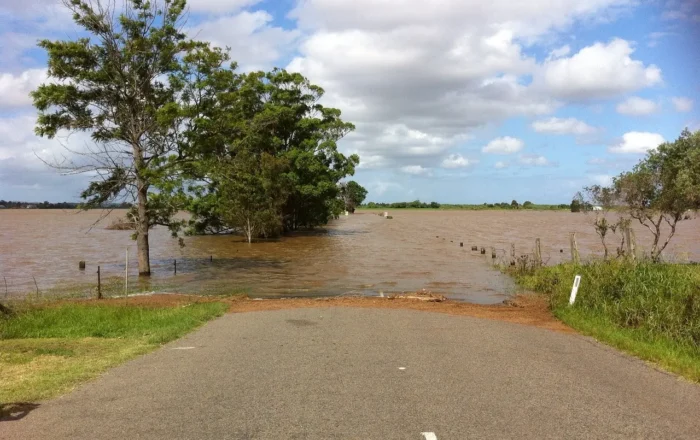

Flooding in Texas is driven by heavy rain, hurricanes, rivers, and rapid urban growth, making it one of the most flood-prone states in the nation.
Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.