Environmental Impact of Nuclear Energy
4 minute readNuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.
Home > Learning Center > Energy Production > Types of Nuclear Reactors: Exploring Nuclear Power Plants
Discover the different types of nuclear power plants and how they work
2 minute read • Last update April 2024

Nuclear reactors generate energy using one of two types of nuclear reactions: fission or fusion. Currently, there are no commercial fusion reactors around the globe because scientists have not yet discovered how to maintain the required temperatures long enough to generate net power.
There several different types of nuclear reactors, including:
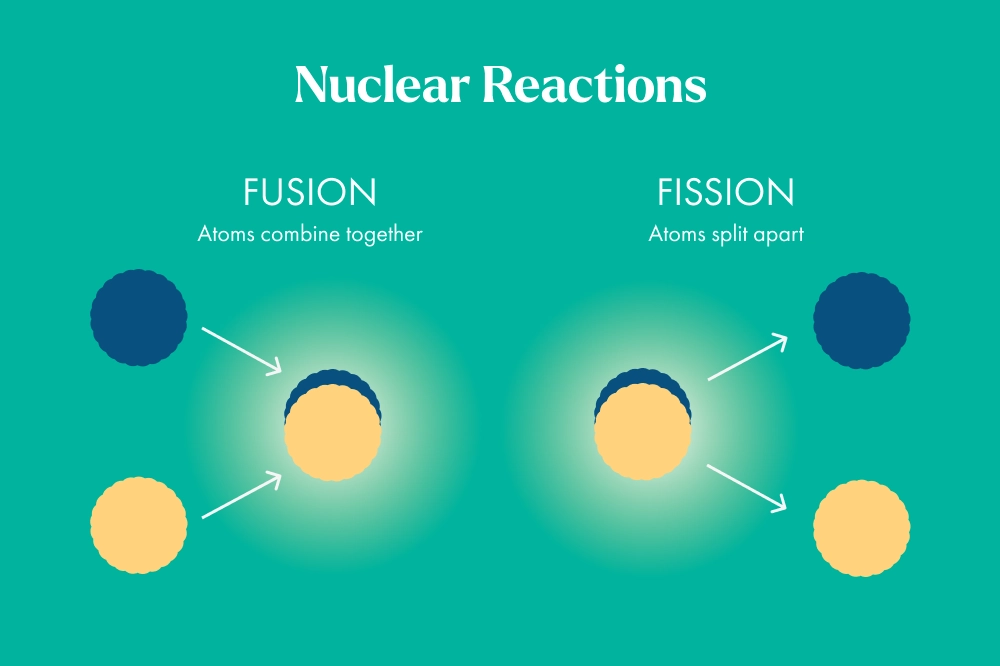
Within the two types of nuclear reactors, there are several more subcategories.
Some of the notable fission reactor designs include:
In PWRs, water acts as both the coolant and moderator. The water is kept under high pressure to prevent boiling, and it transfers heat from the reactor core to a steam generator to produce electricity.
BWRs also use water as both the coolant and moderator. In this design, the water is allowed to boil directly in the reactor core, producing steam that drives the turbine to generate electricity.
HWRs use heavy water, which contains a higher concentration of deuterium, as both the coolant and moderator. Heavy water reactors can utilize natural uranium as fuel and are known for their efficient use of resources.
AGRs use carbon dioxide gas as the coolant and graphite as the moderator. This design is primarily employed in the United Kingdom and is known for its high thermal efficiency.

Two main approaches to achieving fusion reactions are:
MCF uses strong magnetic fields to confine and control a hot plasma of hydrogen isotopes, such as deuterium and tritium. The goal is to achieve conditions where fusion reactions can occur and sustain a self-sustaining plasma state.
ICF involves rapidly compressing and heating fuel pellets using powerful lasers or particle beams. The intense pressure and temperature cause the fuel to undergo fusion reactions. ICF is primarily being explored for its potential use in thermonuclear weapons and as a stepping stone toward achieving practical fusion power.
Graham Lumley, Growth Product Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 10 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

Nuclear energy offers low emissions and reliable power, but it also raises concerns about waste, water use, and safety.

Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.