
Where Electricity Comes From: Generation & Production
Learn how electricity is generated
8 minute read • Last update May 2024

In this article
Electricity, an essential element of modern life, is integral to everything from powering our homes to charging our electronic devices. But what are the processes and sources that contribute to its generation? In this article, we dive deep into the methods and principles of generating energy for electricity and explore the different electricity sources that fuel it.
As we take a closer look at electricity generation, we’ll answer questions such as:
- How do you get electricity?
- Where does electrical energy come from?
- What are some sources of electricity examples?
- Where does electricity come from in the U.S.?
How is electricity generated?
Most electricity is generated from power plants that utilize steam turbines to convert mechanical (also called kinetic) energy into electrical energy. The rotation of the turbine spins the rotor, a set of magnets or electromagnets, inside the core of the stator, a coil of wires. This rotational movement generates a changing electromagnetic field, or voltage, which creates an electric current when run through a conductor. The electric current can then be delivered from the plant via power lines to provide electricity to homes and businesses.
The rotation of the turbines can be fueled from several sources including wind, water, and heat. Keep reading to learn more about the different types of power plants and their fuel sources.

Thermal power plants
Where does most electricity come from? Currently, most of the world’s electricity is produced by thermal power plants that burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, or natural gas to heat water and produce steam. The steam then drives a turbine connected to an electric generator, converting the mechanical energy into electricity.
Hydroelectric power plants
These large power plants can use the energy from flowing or falling water to drive a turbine connected to a generator. The kinetic energy of the moving water is converted into mechanical energy in the turbine and then into electrical energy in the generator.

Wind turbines
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in wind into electrical energy. As the wind turns the blades of the turbine, the mechanical energy generated drives an electric generator.
Solar power plants
Solar power plants convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells. When sunlight hits the PV cells, electrons are knocked loose and flow through the cells, generating an electric current.

Nuclear power plants
In nuclear power plants, nuclear reactions release energy in the form of heat, which is then used to produce steam from water. The steam drives a turbine connected to an electric generator, converting the mechanical energy into electricity. Currently, nuclear power plants are powered by fission reactions (splitting atoms), but scientists are working hard to generate consistent electricity using fusion reactions (combining atoms).
Geothermal power plants
These power plants generate electricity by tapping into the Earth’s internal heat. They use hot water or steam from the Earth’s interior to produce electricity to drive a turbine connected to an electric generator.
Biomass power plants
Biomass power plants burn organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, and animal waste to produce steam. The steam drives a turbine connected to an electric generator, which generates electricity by converting the mechanical energy into electricity.
Ocean energy
This includes both wave power, which uses the energy from waves to generate electricity, and tidal power, which uses the energy from rising and falling tides.
Each method has advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, environmental impact, scalability, and reliability. The choice of method depends on factors such as the availability of resources, the specific needs of the region, and government policies.
Emerging electricity generation technology
Once you know how electricity is generated, it’s important to understand that emerging technologies play a pivotal role in shaping the future of electricity generation. With advancements in materials science, engineering, and technology, newer and more efficient methods of generating electricity are continually being developed. These novel technologies are not only more efficient but also hold the potential to drastically reduce the environmental impact of energy production.
Tidal and wave energy
Tidal power plants use the regular rise and fall of coastal tides to generate electricity. On the other hand, wave energy converters capture the energy of ocean waves, using the up-and-down motion of waves to generate electricity.
Hydrogen fuel cells
Hydrogen fuel cells convert chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct. This clean technology holds promise for various applications, including power generation.
Global and regional electricity trends
Globally, fossil fuels, predominantly coal, have been the leading sources of electricity. However, with rising concerns over climate change, technological advancements, and policy shifts, renewables are making significant strides.
In the United States, for example, the electricity landscape has evolved over time. Historically reliant on coal power, the country has seen a substantial shift towards natural gas electricity generation and renewables, particularly solar and wind power.
Within countries, the primary source of electricity can also vary by region due to factors like resource availability, energy policies, and infrastructure development. Thus, when pondering, “Where does my energy come from?” it is essential to consider regional variations.
Environmental considerations
As the global community grapples with climate change and ecological degradation, the transition to cleaner, renewable sources of energy is becoming increasingly crucial. Fossil fuels, especially coal, are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and other environmental issues.
The shift towards renewables not only reduces carbon emissions but also minimizes other adverse environmental impacts. Wind and solar power, for instance, have a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to fossil fuels.
Challenges and opportunities
Transitioning to a sustainable energy future is a complex endeavor that involves addressing numerous challenges, including:
Intermittency
Solar and wind energy are intermittent sources of renewable generation, dependent on weather conditions. Overcoming this challenge requires innovative energy storage solutions and grid enhancements.
Costs
Although the costs of renewables have decreased dramatically, they can still be higher than fossil fuels in some cases. Continued investment in research and development is needed to drive down costs further.

Infrastructure
Transitioning to renewable energy often requires substantial investments in new infrastructure, including power plants, transmission lines, and storage facilities.
Despite these challenges, the transition to renewable energy offers numerous benefits, including environmental preservation, energy security, and job creation.
Policy and regulatory considerations in electricity generation
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the world’s electricity and generation landscape. They influence the adoption of renewable energy sources, the development of new technologies, and the overall direction of the energy sector.
Promotion of renewable energy
Governments worldwide have implemented policies to promote renewable energy sources like wind, solar panels, and hydropower. These policies include tax incentives, feed-in tariffs, and renewable portfolio standards (RPS). For example, the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) in the United States provides a tax credit for solar energy systems, significantly reducing the cost for homeowners and businesses. Feed-in tariffs guarantee a fixed price for electricity generated from renewable sources, making it more competitive with fossil fuels.
RPS, adopted in many states in the US, require electric utilities to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. These policies have been instrumental in increasing the adoption of more renewable energy resources.
Carbon pricing and emission regulations
Carbon pricing, either through carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, is another policy tool used by governments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By putting a price on carbon, these policies incentivize the reduction of fossil fuel use and promote cleaner energy sources. For example, the European Union’s Emissions Trading System (ETS) has helped reduce emissions by capping the total amount of greenhouse gas companies can emit.
Emission regulations, such as the Clean Air Act in the United States, set limits on pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides emitted by power plants. These regulations have led to the retirement of many coal-fired power plants and spurred investment in cleaner energy sources.
Research and development support
Government support for research and development (R&D) is essential for advancing new energy technologies. Grants, tax credits, and public-private partnerships can help drive innovation in areas like energy storage, smart grids, and advanced nuclear reactors. For example, the US Department of Energy’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) funds high-potential, high-impact energy technologies that are too early for private-sector investment.
Market deregulation
Some governments have deregulated electricity markets to increase competition and drive down prices. In deregulated markets, consumers can choose their electricity provider, leading to more renewable energy options. However, deregulation can also pose challenges, such as price volatility and the need for robust oversight to prevent market manipulation.
Impact on electricity generation
Government policies and regulations significantly impact the electricity generation landscape. By promoting renewable energy, reducing emissions, supporting R&D, and fostering competition, governments can help shape a more sustainable and resilient energy sector. Balancing the needs of consumers, industry, and the environment is essential for achieving a successful energy transition.
Electricity trends, consumption patterns, and other electricity generation statistics
As we analyze the electricity generation trends, energy consumption patterns, and other electricity generation statistics, it is crucial to understand the broader context in which these changes are occurring. The transition to a more sustainable and reliable energy system involves addressing challenges like energy security, affordability, and environmental sustainability while meeting the growing electricity demand. Keeping this context in mind, let’s look closely at each.
Global electricity generation trends
Transition to renewables
There has been a significant shift towards renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower for electricity generation. As of 2022, renewables accounted for nearly 30% of global electricity generation, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
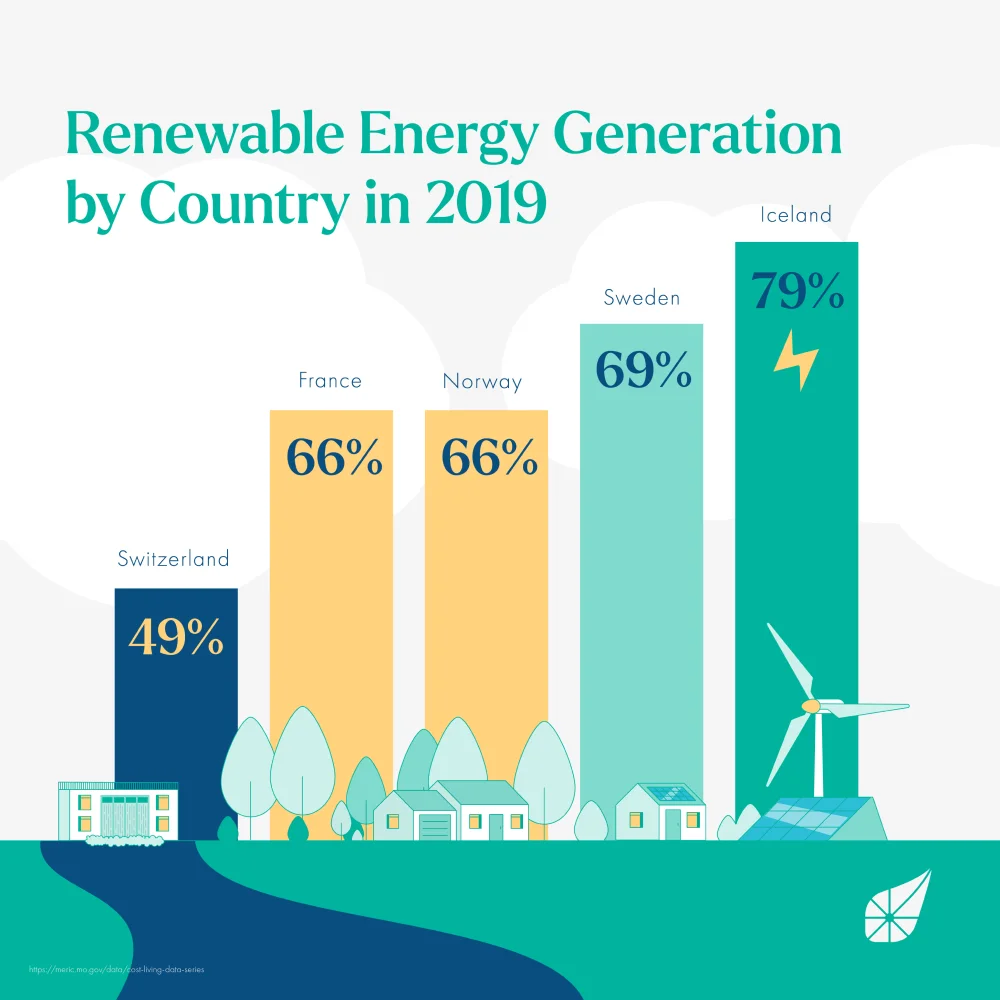
Increasing electrification
Electrification of various sectors, such as transportation and heating, has been a global trend. Electric vehicles and heat pumps have become more popular, increasing the demand for electricity.
Industrial demand
Industry remains a significant consumer of electricity, particularly in sectors like steel, chemicals, and mining.
Residential and commercial use
In the residential and commercial sectors, lighting, appliances, and cooling are the primary electricity consumers. There has been a trend towards greater energy efficiency in these areas.
Electricity generation statistics
Global electricity generation
According to the IEA, global electricity generation in 2022 was around 29,165 TeraWatt-hours (TWh). This represented a 2.2% increase from the previous year.
Renewable electricity generation
Hydropower is the largest source of renewable electricity in the world, followed by wind and solar. The IEA reported that renewable electricity generation increased by 8% in 2022, reaching almost 300 GW.
Coal-fired electricity generation
Coal-fired electricity generation decreased by about 8% in 2022 in the United States. The decline in coal production was offset by a rise in natural gas generation and significant growth in renewable energy sources. Globally, however, coal-fired power generation rose by nearly 2%.
Natural gas-fired electricity generation
The contribution of gas-fired generation to global electricity generation remained largely steady, accounting for over 20% of the total.
Nuclear electricity generation
Nuclear power provided about 10% of the world’s electricity in 2022. In addition, the capacity for nuclear power increased by about 1.5 GW globally. Nuclear power has remained relatively stable as a source of electricity generation, providing a significant share of the electricity in countries like France, the United States, and China.
Choosing an electricity company in Texas
The generation of electricity is a multifaceted process that involves diverse sources and technologies. Understanding the intricacies of electricity generation provides valuable insights into the current energy landscape and the path toward a sustainable future. As the world seeks to address climate change and transition to cleaner energy sources, the choices we make regarding electricity generation will shape the future of our planet.
BKV Energy, as a key player in the Texas energy sector, plays a crucial role in this transition. You can contact the helpful team at BVK Energy anytime to get more information, discuss your electricity needs, and learn about our energy plans.
Written by Graham Lumley
Graham Lumley, Digital Marketing Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 8 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.
Related articles

Is Coal Renewable?
3 minute readCoal is a natural energy source that has played a crucial role in powering human development for centuries. It forms deep within the Earth over millions of years through an intricate process involving the decomposition of plant material under heat and pressure. Despite its natural formation, the process is too…
Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.
