How Many Natural Gas Plants Are in Texas
3 minute readHow many natural gas plants operate in Texas? How many more are proposed amid surging energy demand?
Home > Learning Center > Energy Production > What Is Natural Gas? Everything You Need to Know
9 minute read • Last update May 2024
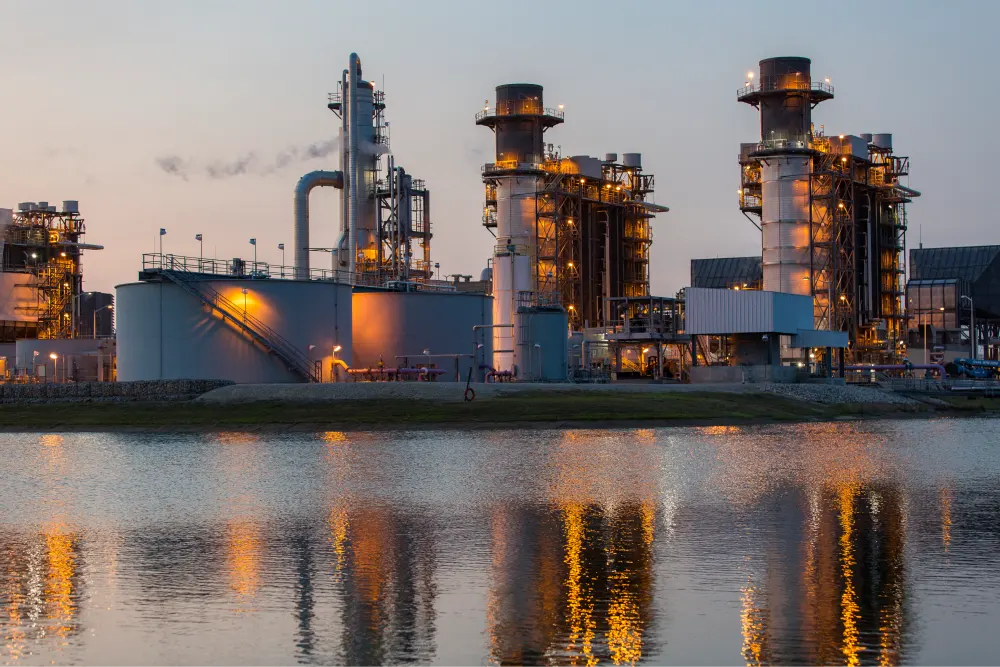

The United States is the world’s largest consumer of natural gas, accounting for about 25% of global consumption by 2020 at around 32.31 trillion cubic feet (Tcf). The electric power sector accounts for around 38% of that growth as consumers are constantly looking for cleaner-burning fuels that lower their carbon footprint in their homes.
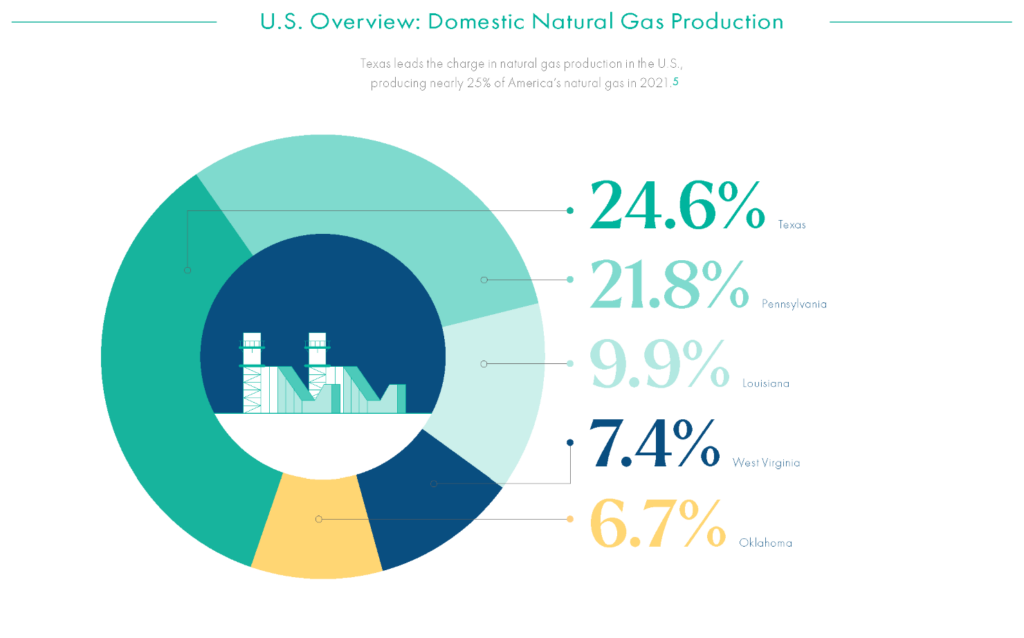
Out of all the states, Texas is the leading producer of natural gas in the US (26% of total production), with over 230 trillion cubic feet of natural gas reserves. Natural gas accounts for more than 40% of the state’s total energy consumption, employs more than 300,000 people, and generates billions of dollars in revenue every year.
But what is natural gas energy? And how does it work? Let’s find out.
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas composed primarily of methane but also contains other gasses such as ethane, propane, butane, and nitrogen. It’s found in underground reservoirs, often associated with oil deposits.
Natural gas has emerged as a significant player in the global energy landscape, offering a cleaner-burning alternative to traditional fossil fuels thanks to its abundant availability, relatively low carbon emissions, and versatility.
Natural gas has become an important primary energy source thanks to the discovery of vast natural gas reserves, advancements in extraction technologies, and increasing environmental concerns that have contributed to its rise.
Today, natural gas is an integral part of the global energy mix, offering a transition away from more carbon-intensive fossil fuels like coal and oil.
Natural gas is a type of fossil fuel that contains various compounds. The primary component of natural gas is methane (CH4), which is made up of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms.
Additionally, natural gas includes smaller amounts of natural gas liquids (NGLs) and non-hydrocarbon gasses like carbon dioxide and water vapor. Natural gas is used as a fuel and plays a role in the production of materials and chemicals.
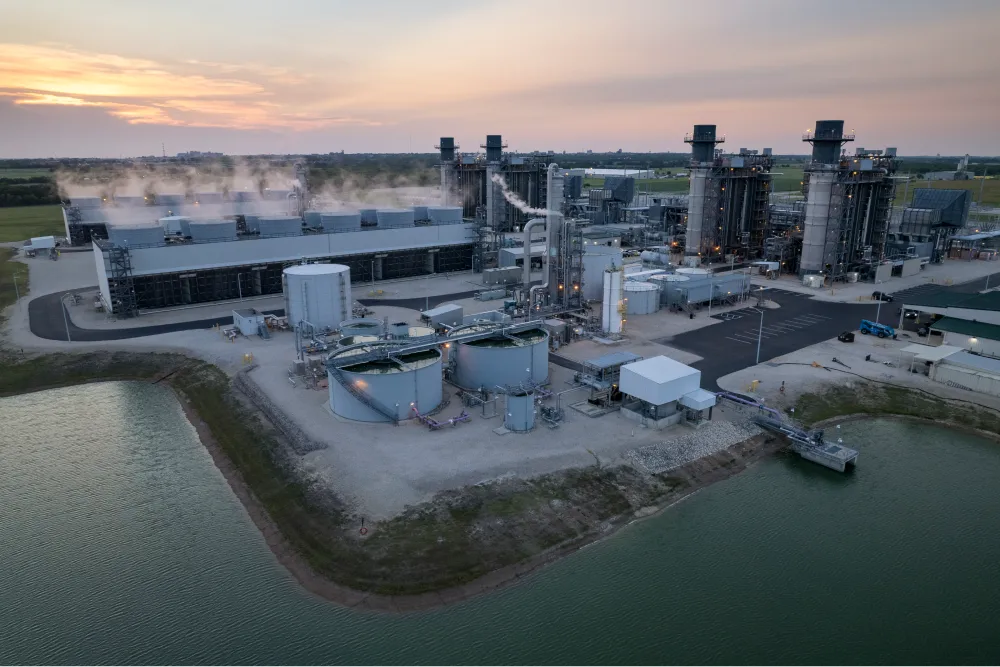

The properties of natural gas (including its high energy content, clean-burning nature, and relatively lower carbon emissions compared to other fossil fuels) make it an attractive choice for power generation, heating, and industrial processes. To harness natural gas as an energy source, it undergoes production and extraction processes.
Natural gas reserves are distributed across the globe, with significant deposits found in various regions. The world’s natural gas reserves are concentrated in a few countries. Russia, Iran, and Qatar have the largest reserves, accounting for about 50% of the world’s total. The United States, United Arab Emirates, Venezuela, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, and Algeria also have significant reserves.
Russia has natural gas reserves of around 38.6 trillion cubic feet, followed by Iran at 32.1 trillion cubic feet and Qatar at 24.7 trillion cubic feet. The US has the fifth largest natural gas reserves in the world, at around 12.9 trillion cubic feet.
Millions to hundreds of millions of years ago, the remains of plants and animals, including diatoms, accumulated in thick layers on the Earth’s surface and ocean floors. Over time, these layers became buried under sand, silt, and rock. Through pressure and heat, some of the carbon and hydrogen-rich material transformed into coal, some into oil (petroleum), and some into natural gas.
Natural gas can be found in different locations. In certain areas, it moved into large cracks and spaces between layers of rock, known as conventional natural gas. In other cases, natural gas occurs within the tiny pores of shale, sandstone, and other
sedimentary rock formations, referred to as shale gas or tight gas, which is considered unconventional natural gas.
Natural gas is also associated with crude oil deposits, and this type of natural gas is called associated natural gas. It can be found on land, offshore, and deep under the ocean floor. Natural gas found in coal deposits is known as coalbed methane.
To find natural gas, geologists study the structure and processes of the Earth. They identify geologic formations that are likely to contain natural gas deposits. Seismic surveys, conducted on land and in the ocean, help locate the right places to drill natural gas wells.
These surveys create and measure seismic waves to gather information about the rock formations below the surface. If a site shows potential for producing natural gas, an exploratory well is drilled and tested to determine the quantity and quality of the natural gas resource.
When natural gas is found and deemed economically viable, one or more production wells are drilled. In conventional natural gas deposits, the gas flows easily up through the wells to the surface.
However, in some countries, including the United States, shale gas and other sedimentary rock formations are accessed through hydraulic fracturing or fracking. This process involves injecting water, chemicals, and sand at high pressure to break up the rock formation, releasing the natural gas. The gas is then collected in gathering pipelines and sent to processing plants.
Natural gas undergoes processing before It’s sold and consumed. Wet natural gas, which is withdrawn from wells, contains methane along with natural gas liquids (NGLs) and water vapor. At processing plants, water vapor and non-hydrocarbon compounds are removed, and NGLs are separated and sold separately. The remaining natural gas, called dry, consumer-grade, or pipeline-quality natural gas, is sent through pipelines for storage or distribution to consumers. Odorants are added to natural gas pipelines to help detect leaks. In cases where natural gas pipelines are unavailable, associated natural gas may be reinjected into oil wells, vented, or burned.
The majority of natural gas consumed in the United States is produced domestically, with some imports from Canada and Mexico. Additionally, a small amount of natural gas is imported in liquefied form (liquefied natural gas or LNG).
According to the US Energy Information Administration, natural gas emits about 49% less CO2 than coal and about 30% less CO2 than oil. But while natural gas is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to coal and oil, its production and extraction can still have environmental and social impacts.
Methane emissions during production and transportation, water usage and contamination risks, habitat disruption, and community concerns are some of the environmental and social challenges associated with natural gas production.
The good news is that the CO2 emissions from natural gas can be reduced by using technologies such as carbon capture and storage.
Natural gas energy has several uses that make it a valuable resource in various sectors, including:
One of the primary uses of natural gas is for generating electricity. Natural gas power plants use turbines that are fueled by burning natural gas. The heat produced from the combustion process is used to spin the turbines, which then generate electricity.
Natural gas power plants are known for their efficiency and relatively low emissions compared to other fossil fuel-based power plants. They play a significant role in providing electricity to homes, businesses, and industries.
Natural gas is widely used for heating purposes in both residential and industrial settings. In homes, natural gas is commonly used for heating indoor spaces, heating water for showers and other household activities, and powering gas stoves for cooking. Industries rely on natural gas for processes that require high-temperature heat, such as manufacturing, food processing, and heating large spaces like warehouses and factories.
Natural gas can also be used as an alternative fuel for transportation. Vehicles can be equipped with natural gas engines that run on compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Natural gas vehicles produce lower emissions compared to gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles, which contributes to reduced air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. They are also more fuel-efficient, which can save money on fuel costs. In addition, natural gas-powered vehicles are quieter than diesel-powered vehicles, which can reduce noise pollution.
Amtrak operates a fleet of natural gas-powered locomotives that are used to pull passenger trains on a variety of routes across the country, while PG&E operates a fleet of natural gas-powered buses that are used to provide public transportation in California.
Natural gas-powered trains and buses offer a number of advantages over traditional diesel-powered vehicles. They produce fewer emissions, which can help to improve air quality.
Natural gas contains hydrocarbons that can be used as raw materials for producing various chemicals and materials and serve as a fundamental resource for the production of plastics, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and other essential products.
Natural gas consumption is growing at an average rate of 2.1% per year in the United States as more and more Americans discover its benefits, which include:
Compared to other fossil fuels like coal and oil, natural gas has a lower environmental impact. When burned for power generation, natural gas produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO2) and air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). It helps to reduce air pollution and mitigate the effects of climate change. Natural gas emits about 49% less carbon dioxide (CO2) than coal and about 30% less CO2 than oil.
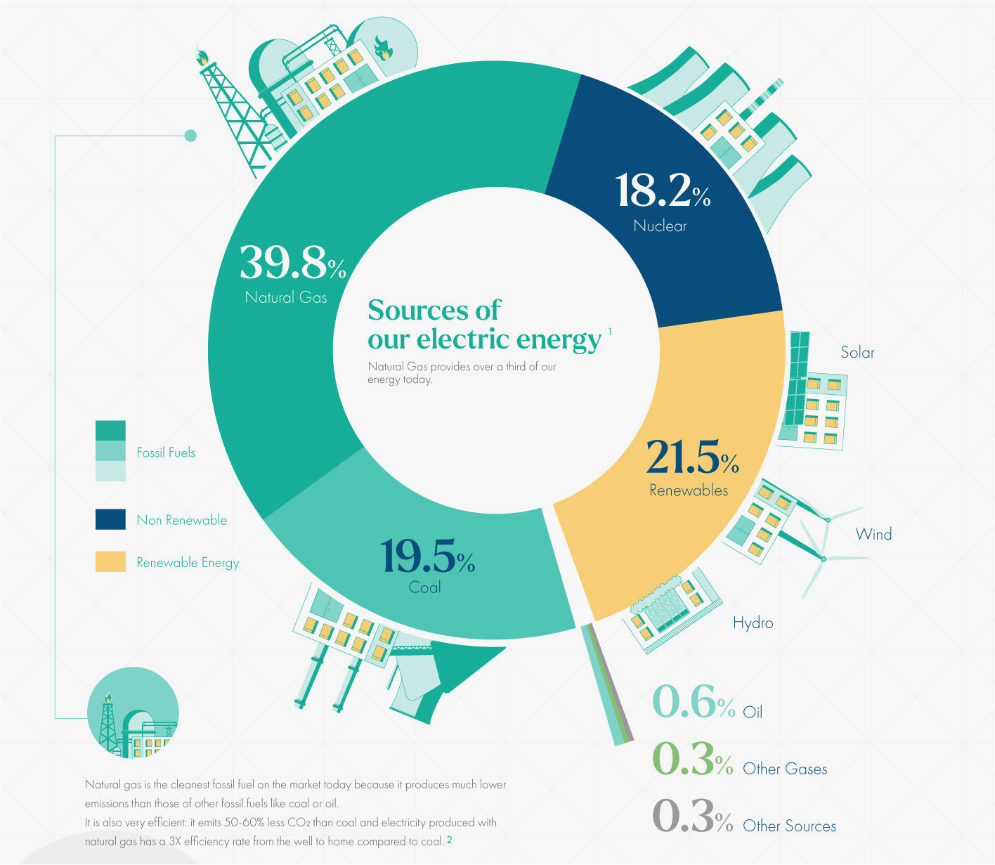
Natural gas power plants are highly efficient in converting fuel into electricity. They have a higher energy conversion rate compared to coal-fired power plants, resulting in less wasted energy. The efficiency of natural gas power generation helps in reducing fuel consumption and operating costs, making it an economically viable option.
Natural gas is a versatile energy source with various applications beyond power generation. It’s widely used for heating homes, buildings, and industrial processes. It’s also utilized as a fuel for cooking, water heating, and even in some transportation sectors as an alternative fuel.
While natural gas offers advantages, it also faces challenges and controversies that need to be addressed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with natural gas is methane leaks. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release during natural gas production and distribution can contribute to climate change. The extraction method of hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, has raised concerns about water contamination and potential damage to ecosystems.
The reliance on natural gas from specific regions can create geopolitical challenges and energy security issues. Countries heavily dependent on natural gas imports may face vulnerability to supply disruptions or price fluctuations. Diversification of energy sources and development of domestic resources can help mitigate these risks.
While natural gas produces fewer emissions compared to other fossil fuels, It’s still a carbon-intensive energy source. The challenge lies in balancing the need for energy security with the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and achieving a sustainable energy future.
The natural gas industry is continuously exploring new technologies and innovations to address environmental concerns and enhance efficiency. Let’s explore some notable advancements:
Renewable natural gas (RNG), also known as biomethane, is produced from organic waste sources such as landfills, wastewater treatment plants, and agricultural waste. It offers a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to conventional natural gas. Research is underway to explore other clean gas alternatives, such as hydrogen produced from renewable sources, to further reduce carbon emissions.
Carbon capture, use, and storage (CCUS) technologies aim to capture carbon dioxide emissions from natural gas power plants and store them underground or repurpose them for industrial use. CCUS has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with natural gas power generation.
The development of smarter grid technologies is making it easier for natural gas power plants to work together with renewable energy sources. These advancements help to balance the electricity grid and make sure that energy is distributed efficiently. With the help of advanced monitoring and control systems, natural gas power plants can change how much energy they produce based on how much renewable energy is available at any given time. This helps to keep the grid stable and reliable, even when there are fluctuations in renewable energy generation.
What is natural gas energy? It’s a viable, affordable, and cleaner energy source that will power the world for the foreseeable future. While there are challenges, companies are working hard to reduce the risks and offset their carbon emissions even further.
As the global economy grows, so does the demand for energy. Natural gas is an affordable and reliable source of energy, making it a good choice for meeting this demand. There have also been significant developments in the development of new natural gas resources, such as shale gas. This has led to an increase in the supply of natural gas, which has helped to keep prices low and made natural gas more affordable.
Currently, the United States is the world’s largest consumer of natural gas (30 trillion cubic feet), followed by Russia and China. These three countries account for about 50% of global natural gas consumption. Japan is currently using 10.3 trillion cubic feet of natural gas per annum, whereas India (8.9 trillion cubic feet) and Germany (7.4 trillion cubic feet) follow closely behind.
Natural gas can play a role in the transition to a low-carbon energy system. This is because natural gas produces fewer emissions of greenhouse gasses than coal and oil. Natural gas can be used to generate electricity with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. CCS technology captures the carbon dioxide produced when natural gas is burned and stores it underground. This helps to reduce the emissions of greenhouse gasses from natural gas-fired power plants.
Natural gas is a fossil fuel. But power generated from natural gas emits about half as much carbon as the same amount of power generated from coal. Even though natural gas is a fossil fuel, it can be an important bridge fuel that can help us to transition to a low-carbon energy system.
Geopolitical considerations are significant in natural gas energy production and distribution. Countries with abundant natural gas reserves often have a strategic advantage in terms of energy security and can become major players in the global energy market.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022 has led to concerns about European energy security, as Russia is a major supplier of natural gas to Europe. We’ve also seen conflicts in the Middle East disrupt natural gas production and distribution in the region, which has had a significant impact on the global energy market.
According to the American Petroleum Institute, there were approximately 9.8 million jobs in the United States in 2021 that were directly or indirectly related to the natural gas industry. This number includes jobs in the upstream, midstream, and downstream sectors of the industry.
Advancements in technology are being made to improve the efficiency and sustainability of natural gas energy. These include innovations in the extraction process, such as more environmentally friendly methods of hydraulic fracturing. Additionally, research is being conducted to develop carbon capture and storage technologies that can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from natural gas power plants.
The current global demand for natural gas energy is about 4.1 trillion cubic feet per year. This demand is expected to grow by about 2% per year over the next 20 years, reaching about 5.2 trillion cubic feet per year by 2040. As countries around the world seek cleaner and more efficient energy sources, the demand for natural gas is expected to increase in the future.
Graham Lumley, Growth Product Manager at BKV Energy, leads digital and traditional marketing strategies, focusing on educating Texans about the state's deregulated energy market. With over 10 years of marketing experience, he creates content to help consumers understand and save on their energy bills, bringing a fresh and dynamic approach to the industry.

How many natural gas plants operate in Texas? How many more are proposed amid surging energy demand?

Get $50 off your electric bill!
Use code BKVEJOINUS50
Enter your zip code to shop BKV Energy's affordable, fixed-rate Texas electricity plans. Use the promo code for $50 off your electric bill.